Input Output Monitor (IOM)
The Input Output Monitor (IOM) module serves as a smart I/O comparison unit, observing and checking for the correct operation of system peripheral outputs that may serve and/or control externally-attached hardware, as well as the correct operation of the hardware itself, including any sensors whose signals may serve as an input to the monitoring function.
Feature list
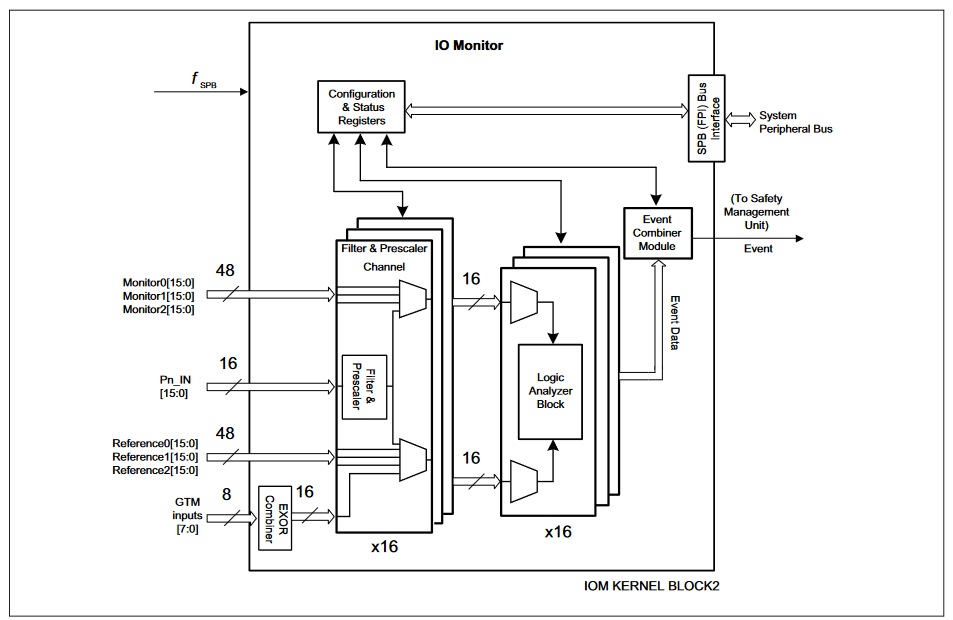
- Sixteen filter and pre-scaler channels, each connected to a specific pad (PIN), the output of which to serve as a monitor or reference signal
- Sixteen logic analyzer modules (LAMs), where each channel includes a multiplexer for independent selection of monitor and reference signal inputs with which the comparison is performed. A local event (that is, internal to the IOM) is generated when the timing relationships between the selected monitor and reference signals are violated. Configurable via register settings
- One EXOR combiner, configurable (via register) to select a range of up to eight GTM inputs to generate a combined signal to serve as a reference
- Event combiner module (ECM), that takes the 16 local event signals (1 from each of the LAM modules) and generates a system event signal (connecting to a system safety management unit) from a single, combination, or multiple local event(s). Configurable via register settings
- System peripheral bus (SPB) interface for configuration and status register interaction
Functional description
The input output monitor (IOM) module serves as a smart I/O comparison unit, observing and checking for the correct operation of system peripheral outputs that may serve and/or control externally attached hardware, as well as the correct operation of the hardware itself, including any sensors whose signals may serve as an input to the monitoring function. The monitoring function may be achieved in a number of configurable ways depending upon the application and the type of safety measure to be deployed.
Monitoring and reference signals are taken from the appropriate system peripherals (for example, capture/compare units and general-purpose timer units) where they are connected to the internal pad logic that may or may not be driven to the pads (configuration dependent). A connection can be made to a signal that is to be controlled externally and to another signal that can serve as a reference, although it must not be controlled outside the chip. A driven signal can also serve as a reference to compare with another signal that can be provided via a GPIO input, for example, from a sensor outside the device. Up to 16 monitoring points can be configured, with the capability to generate a system event that may be driven from one individual, several individual or multiple occurrences of a monitored condition, or a combination of several depending upon configuration.
The input output monitor (IOM) has the following interfaces:
- System peripheral bus (SPB) - for configuring the components of the IOM and querying the associated status registers/bit fields
- Multiple port logic/module connectivity, serving as reference or monitor signals
- Safety management unit (SMU) - a single global event signal used to inform the SMU of a generated event within the IOM
The functionality of the IOM is independent of the system debug, and no connectivity or operating mode. The operating mode exists for this purpose. In addition to the logic analyzer modules, filter and pre-scaler blocks and event combiner module, the IOM also provides a system peripheral bus (SPB) interface for accessing configuration and status registers.