General OpenOCD commands
version
Displays a string identifying the OpenOCD version.
Example:
openocd -c "version; shutdown"
help
With no parameters, prints help text for all commands. Otherwise, prints each help-text-containing string. Not every command provides help text.
help [string]
Example:
openocd -c "help; shutdown"
shutdown
Closes the OpenOCD server, disconnecting all clients (GDB, telnet, other). If the
error
option is used, OpenOCD will return non-zero exit code to the parent process.
shutdown [error]
Example:
openocd -c "shutdown error"
log_output
Redirects logging to the filename; the initial log output channel is
stderr
.
log_output [filename]
Example:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "log_output d:/log.txt; targets; shutdown"
debug_level
Displays the debug level. If
n
(from 0..3) is provided, set it to that level.
This affects the kind of messages sent to the server log:
Level 0: Error messages only
Level 1: Level 0 messages + warnings
Level 2: Level 1 messages + informational messages
Level 3: Level 2 messages + debugging messages
The default is Level 2, but that can be overridden on the command line along with the location of that log file (which is normally the server's standard output).
debug_level [n]
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
This example sets the debug level to L3 at the start of the target initialization, then switches to L1 for programming operation.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "debug_level 3; init; reset init; debug_level; program c:/firmware/firmware.hex verify; shutdown"
reset_config
Displays or modifies the reset configuration of your combination of the board and target.
reset_config <mode_flag> ...
The
mode_flag
options can be specified in any order, but only one of each type –
signals
,
combination
,
gates
,
trst_type
,
srst_type
and
connect_type
– may be specified at a time. If you don't provide a new value for a given type, its previous value (perhaps the default) remains unchanged.
For example, do not say anything about TRST just to declare that if the JTAG adapter should want to drive SRST, it must explicitly be driven HIGH (
srst_push_pull
).
The
signals
option specifies which of the reset signals is/are connected.
For example, If the board doesn't connect SRST provided by the JTAG interface properly, OpenOCD cannot use it. The possible values are:
none (default)
trst_only
srst_only
trst_and_srst
See the
OpenOCD documentation
for details.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
This example configures the reset configuration to trst_and_srst for the target MCU.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "reset_config trst_and_srst; targets; shutdown"
adapter speed
Sets a non-zero speed in kHz for the debug adapter. Therefore, to specify 3 MHz, provide
3000
.
adapter speed <max_speed_kHz>
JTAG interfaces usually support a limited number of speeds. The speed actually used will not be faster than the speed specified. Chip datasheets generally include a top JTAG clock rate. The actual rate is often a function of a CPU core clock, and is normally lower than that peak rate.
For example, most Arm® cores accept up to one sixth of the CPU clock. Speed 0 (kHz) selects the RTCK method. If your system uses RTCK, you will not need to change the JTAG clocking after a setup.
Example:
This example configures SWD transport and sets the clock for J-Link to 2 MHz.
openocd -s ../scripts -c "transport select swd” -f interface/jlink.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; adapter speed 2000; program c:/firmware/firmware.hex verify; shutdown"
adapter serial
Specifies the serial number of the adapter device to use, and can be used to specify which device to use if multiple devices are connected to the host PC. If not specified, serial numbers are not considered.
adapter serial <serial_number>
Example:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -c "adapter serial 1A1509F301237400; shutdown"
transport list
Displays the names of the transports supported by this version of OpenOCD.
Example:
openocd -c "transport list; shutdown"
transport select
Selects which of the supported transports to use in this OpenOCD session.
transport select <transport_name>
When invoked with the
transport_name
option, OpenOCD attempts to select the named transport. The transport must be supported by the debug adapter hardware and by the version of OpenOCD you are using (including the adapter's driver). If no transport has been selected and no
transport_name
is provided, transport select auto-selects the first transport supported by the debug adapter.
transport select
always returns the name of the session's selected transport, if any.
Example:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/jlink.cfg -c "transport select jtag"
targets
With no parameter, this command displays a table of all known targets in a user-friendly form. With a parameter, this command sets the current target to a given target with a given
name
; this is relevant only to boards with more than one target.
targets [name]
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Displays all available targets of the connected PSOC™ Edge MCU:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "targets; shutdown"
Selects the SYS AP of the PSOC™ Edge MCU as the current target:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "targets cat1d.sys; target current"
scan_chain
Displays the TAPs in the scan chain configuration, and their status. (Do not confuse this with the list displayed by the
targets
command. That only displays TAPs for CPUs configured as debugging targets.)
Example (J-Link & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/jlink.cfg -c "transport select jtag; adapter speed 1000; init; scan_chain; shutdown"
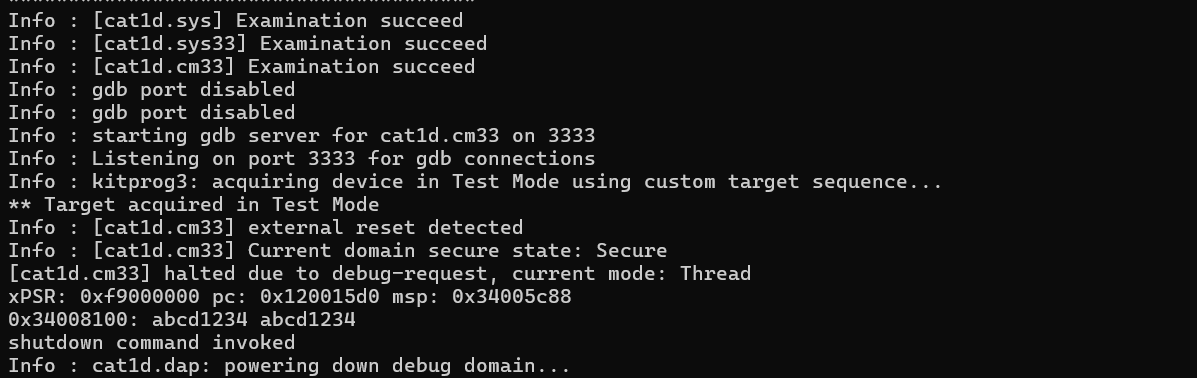
md(w)(h)(b)
Displays the contents of address addr, as 32-bit words (
mdw
), 16-bit half-words (
mdh
), or 8-bit bytes (
mdb
).
mdw [phys] <addr> [count]
mdh [phys] <addr> [count]
mdb [phys] <addr> [count]
When the current target has a present and active MMU,
addr
is interpreted as a virtual address. Otherwise, or if the optional
phys
flag is specified,
addr
is interpreted as a physical address. If
count
is specified, it displays that many units; otherwise, only one item is displayed.
Example KitProg3 + PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Displays two 32-bit words of memory of the PSOC™ Edge MCU.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; mdw 0x34008100 2; shutdown"
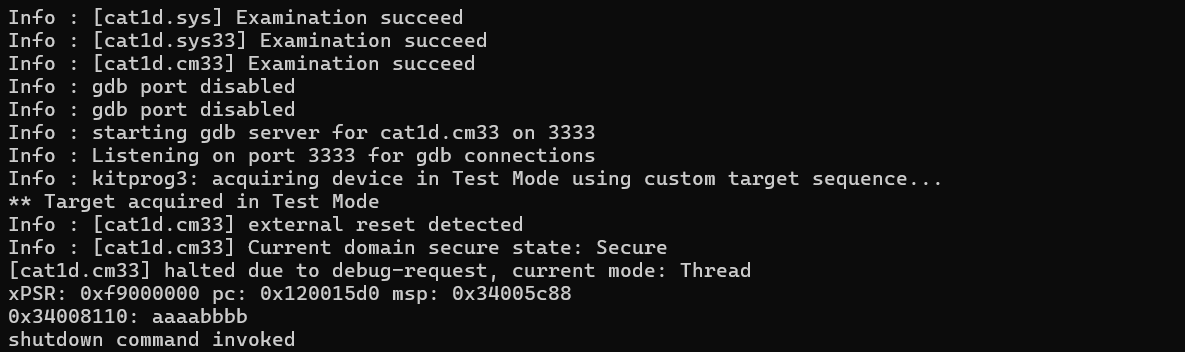
mw(w)(h)(b)
Writes the specified
word
(32 bits),
halfword
(16 bits), or
byte
(8-bit) value at the specified address
addr
.
mww [phys] <addr> <word>
mwh [phys] <addr> <halfword>
mwb [phys] <addr> <byte>
When the current target has a present and active MMU,
addr
is interpreted as a virtual address. Otherwise, or if the optional
phys
flag is specified,
addr
is interpreted as a physical address.
Example (KitProg3 + PSOC™ Edge MCU target):
Write a 32-bit word to the memory of the PSOC™ Edge MCU.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; mww 0x34008110 0xAAAABBBB; mdw 0x34008110; shutdown"
init
This command terminates the configuration stage and enters the run stage. This helps to have the startup scripts manage tasks such as resetting the target and programming flash. To reset the CPU upon a startup, add init and reset at the end of the config script or at the end of the OpenOCD command line using the -c command line switch.
If this command does not appear in any startup/configuration file, OpenOCD executes the command for you after processing all configuration files and/or command-line options.
Note:
This command normally occurs at or near the end of your config file to force OpenOCD to initialize and make the targets ready. For example: If your config file needs to read/write memory on your target, initialization must occur before the memory read/write commands.
Example (KitProg3 + PSOC™ 6 MCU target):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; shutdown"
reset [run] [halt] [init]
Performs as hard a reset as possible, using SRST if possible. All defined targets will be reset, and target events will fire during the reset sequence.
The optional parameter specifies what should happen after a reset. If there is no parameter, a reset run is executed. The other options will not work on all systems. See
reset_config
.
run
– Let the target run
halt
– Immediately halt the target
init
– Immediately halt the target, and execute the reset-init script
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; shutdown"
program
Programs a given programming file in the HEX, SREC, ELF, or BIN formats into the flash of the target device.
program <filename> [preverify] [verify] [reset] [exit] [offset]
The only required parameter is
filename
; others are optional.
preverify– Performs the verification step before flash programming. Programming will be skipped if the flash contents match the data file.verify– Compares the contents of the data file filename with the contents of the flash after flash programmingreset
– "reset run" is called if this parameter is given (see
reset [run] [halt] [init]
for details)
exit
– OpenOCD is shut down if this parameter is given.
offset– If relocation offset is specified, it is added to the base address for each section in the image.
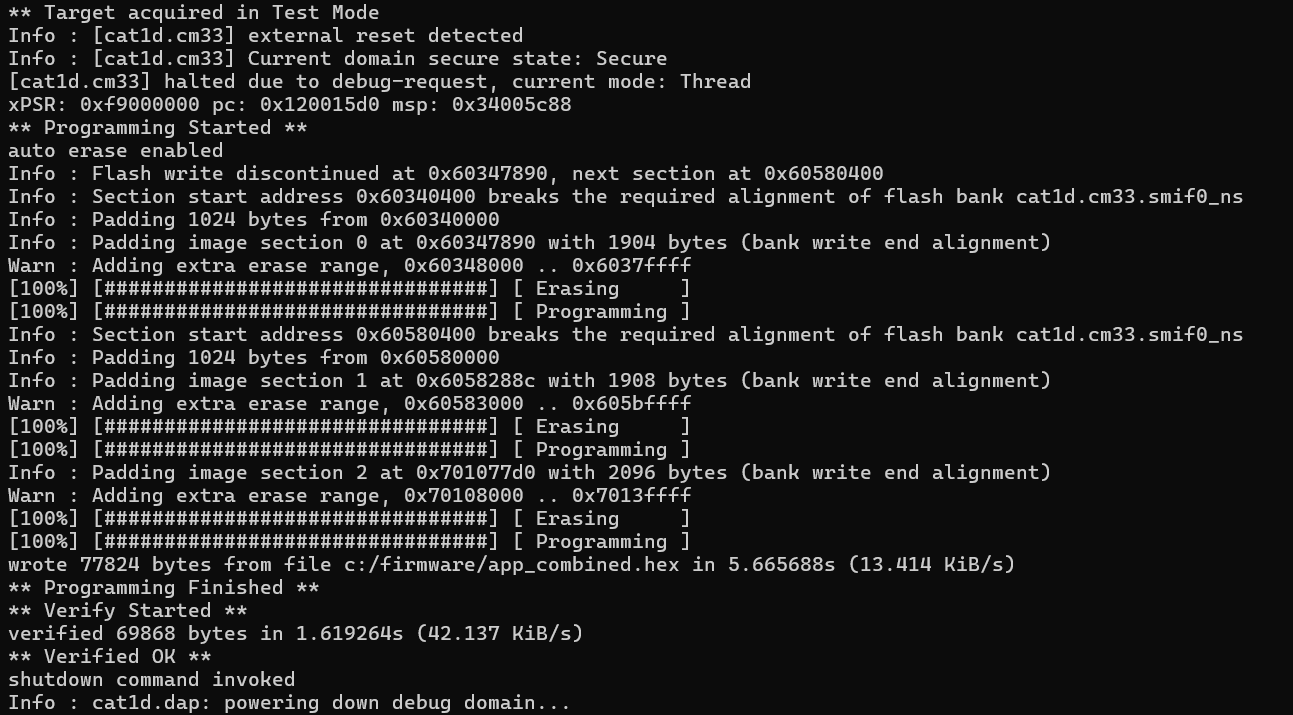
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
This example specifies QSPI configuration and and connects to the KitProg3 probe with the PSOC™ Edge MCU target, programs flash with the
app_combined.hex
file, verifies programmed data, and finally shuts down the OpenOCD programmer.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -c "set SMIF_BANKS { 0 {addr 0x60000000 size 0x01000000 psize 0x00000200 esize 0x00040000} }" -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "program c:/firmware/app_combined.hex verify exit"
erase_all
This command erases the flash memory. Some SFlash rows could be skipped due to restrictions, see
psoc6/cat1c/traveo2/xmc5xxx sflash_restrictions
command.
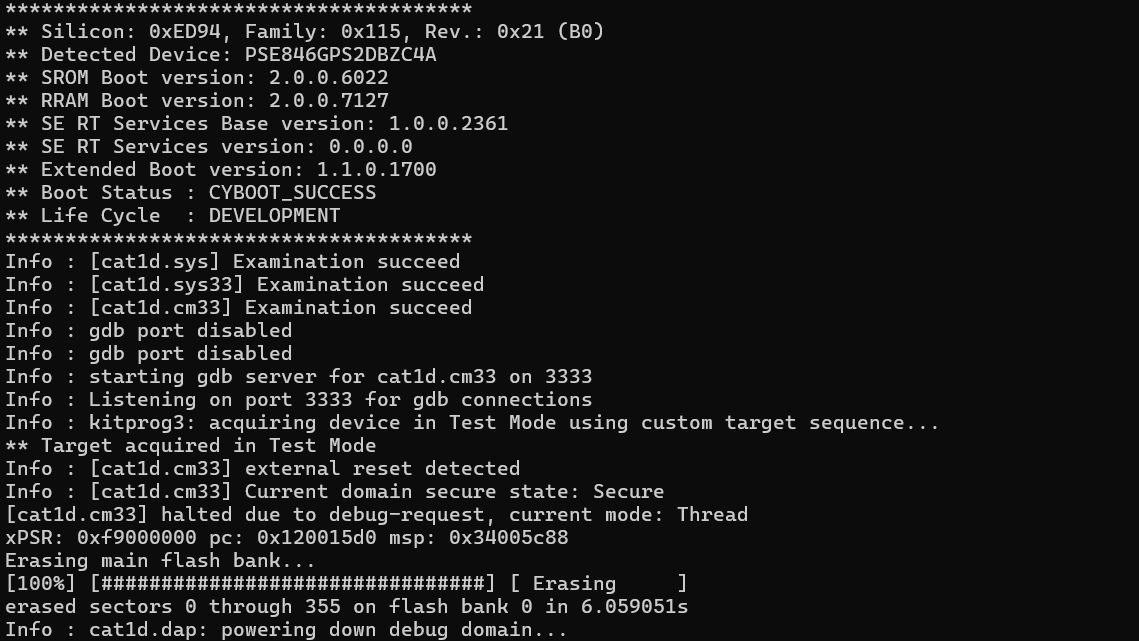
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ 6 MCU target):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; erase_all; exit"
flash banks
Prints a one-line summary of each flash bank of the target device.
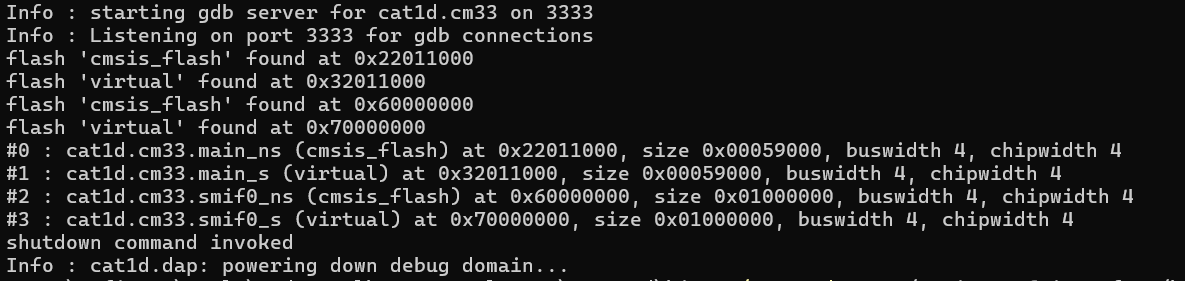
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ 6 MCU):
./openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -c "set SMIF_BANKS { 0 {addr 0x60000000 size 0x01000000 psize 0x00000200 esize 0x00040000} }" -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; flash probe 0; flash probe 1; flash probe 2; flash probe 3; flash banks; shutdown"
flash info
flash info <num> [sectors]
Prints info about the flash bank
num
, a list of protection blocks and their status. Uses sectors to show a list of sectors instead. The
num
parameter is a value shown by flash banks. This command will first query the hardware; it does not print cached and possibly stale information.
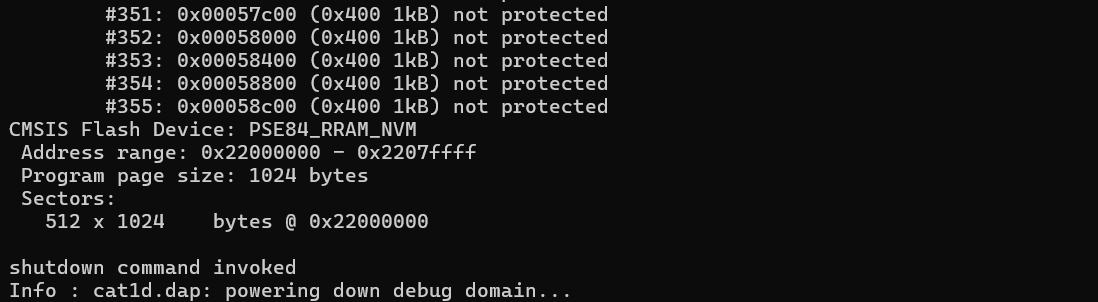
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash info 0; shutdown"
Prints the information about flash bank 0:
flash protect
Enables (
on
) or disables (
off
) protection of flash blocks in flash bank
num
, starting at protection block
first
and continuing up to and including
last
.
Note:
This command is applicable for PSOC™ 4 MCU only.
flash protect num first last (on|off)
Providing a
last
block of last specifies "to the end of the flash bank". The
num
parameter is a value shown by flash banks. The protection block is usually identical to a flash sector. Some devices may utilize a protection block distinct from the flash sector. See
flash info
for a list of protection blocks.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ 4 MCU):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/psoc4.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash protect 0 0 last on; shutdown"
Protect all sectors from being written in flash bank 0:
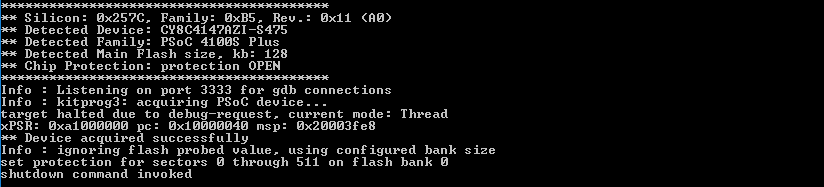
flash erase_sector
Erases sectors in the bank
num
, starting at Sector
first
up to and including Sector
last
.
flash erase_sector <num> <first> <last>
Sector numbering starts at 0. Providing the last sector of
last
specifies "to the end of the flash bank". The
num
parameter is a value shown by flash banks.
Note:
On PSOC™ 4, PSOC™ 4 HVPA, and PSOC™ 4 HVMS MCU devices, per-sector erase operation is not supported, only mass-erase is available. This command is ignored on the device unless a full erase of the flash is requested (flash erase_sector 0 0 last).
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash erase_sector 0 0 last; shutdown"
Erases all sectors in flash bank 0:
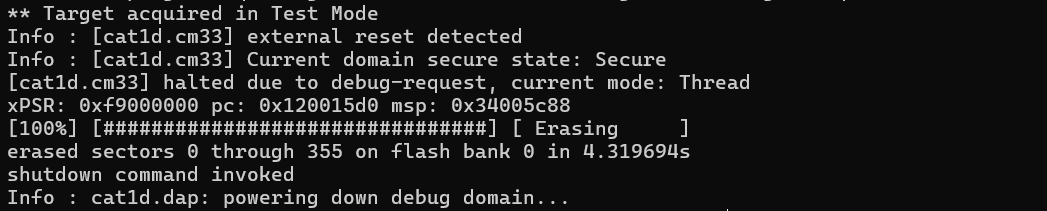
flash erase_address
Erases the sectors starting at
address
for the
length
bytes.
flash erase_address [pad] [unlock] <address> <length>
Unless
pad
is specified,
address
must begin a flash sector, and
address + length - 1
must end a sector. Specifying
pad
erases the extra data at the beginning and/or end of the specified region, as needed to erase only full sectors. The flash bank to use is inferred from the
address
, and the specified
length
must stay within that bank. As a special case, when
length
is zero and
address
is the start of the bank, the whole flash is erased. If unlock is specified, the flash is unprotected before erase starts.
Note:
On PSOC™ 4, PSOC™ 4 HVPA, and PSOC™ 4 HVMS MCU devices, per-sector erase operation is not supported, only mass-erase is available. This command is ignored on the device unless a full erase of the flash is requested (e.g.,
flash erase_address 0 65536
for 64 KB parts).
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
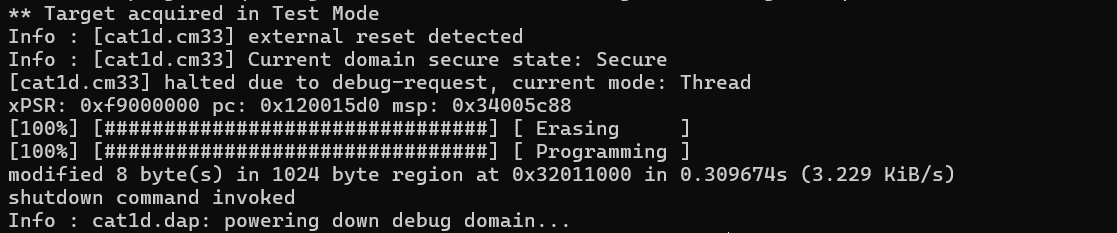
In this example, OpenOCD erases the 2-KB block starting at address 0x32011000:
kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash erase_address 0x32011000 2048; shutdown"
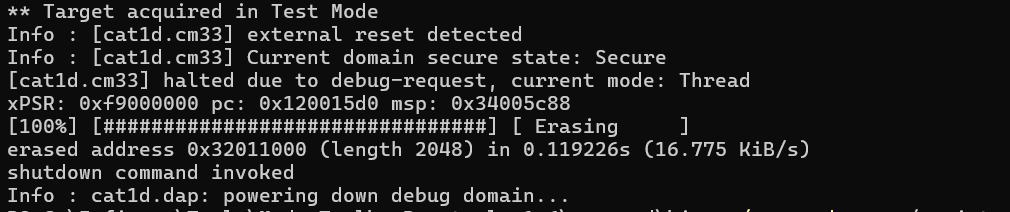
flash write_bank
Writes the binary
filename
to flash bank
num
, starting at
offset
bytes from the beginning of the bank.
flash write_bank <num> <filename> <offset>
The
num
parameter is a value shown by flash banks.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Writes the binary file
firmware.bin
to flash bank 0 with starting at offset 0:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/cy8c6xxx.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash write_bank 0 d:/firmware.bin 0x0; shutdown"
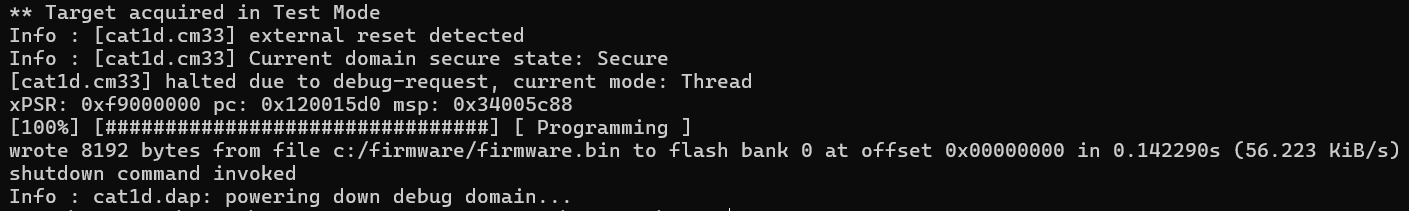
flash write_image
Writes the image
filename
to the current target's flash bank(s).
flash write_image [erase] [unlock] <filename> [offset] [type]
Only loadable sections from the image are written. If a relocation
offset
is specified, it is added to the base address for each section in the image. The file [
type
] can be specified explicitly as
bin
(binary),
ihex
(Intel hex),
elf
(ELF file), or
s19
(Motorola s19). The relevant flash sectors will be erased prior to programming if the erase parameter is given. If
unlock
is provided, the flash banks are unlocked before
erase
and
program
. The flash bank to use is inferred from the address of each image section.
Attention:
Be careful using the erase flag when the flash is holding data you want to preserve. Portions of the flash outside those described in the image's sections might be erased with no notice.
When a section of the image being written does not fill out all the sectors it uses, the unwritten parts of those sectors are necessarily also erased, because sectors cannot be partially erased.
Data stored in sector "holes" between image sections are also affected. For example,
flash write_image erase ...
of an image with one byte at the beginning of a flash bank and one byte at the end erases the entire bank – not just the two sectors being written.
Also, when flash protection is important, you must reapply it after it has been removed by the
unlock
flag.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Writes the ELF image
firmware.hex
to the PSOC™ Edge MCU:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash write_image erase c:/firmware/firmware.hex; shutdown"
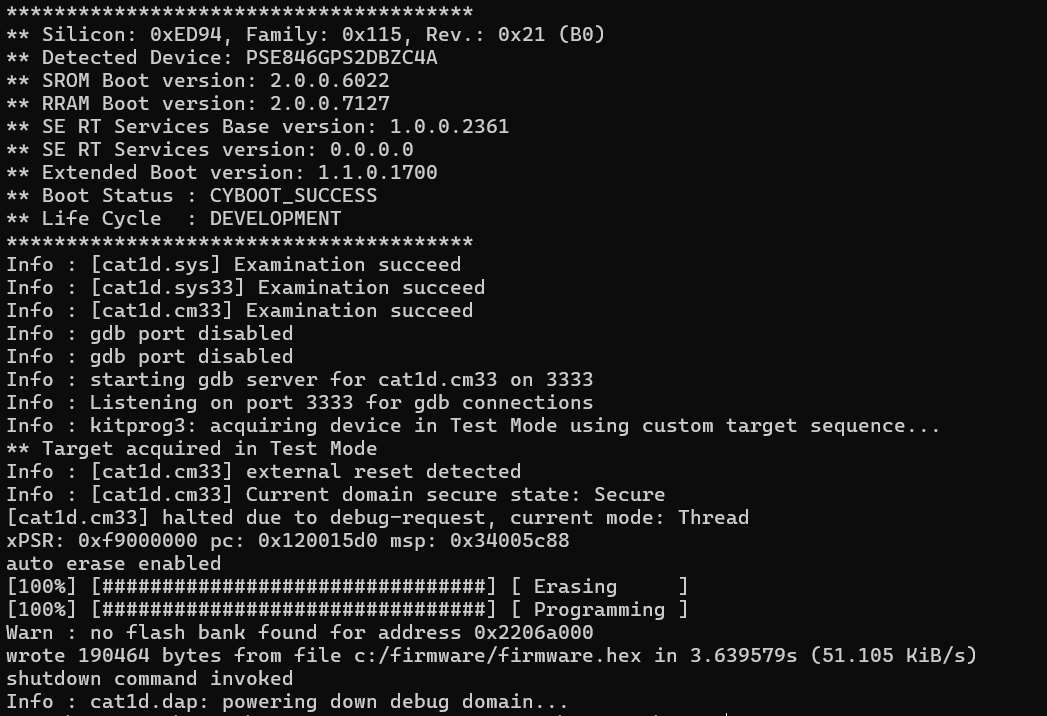
flash fill(w)(h)(b)
Fills the flash memory with the specified word (32 bits), half-word (16 bits), or byte (8-bit) pattern, starting at address and continuing for length units (word/half-word/byte).
flash fillw <address> <word> <length>
flash fillh <address> <halfword> <length>
flash fillb <address> <byte> <length>
No
erase
is done before writing; when needed, that must be done before issuing this command. Writes are done in blocks of up to 1024 bytes, and each
write
is verified by reading back the data and comparing it to what was written. The flash bank to use is inferred from the address of each block, and the specified length must stay within that bank.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Fills the 32-KB block of memory starting at address 0x32011000 with the pattern 0x5A:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash fillw 0x32011000 0x5A5A5A5A 0x00002000; shutdown"
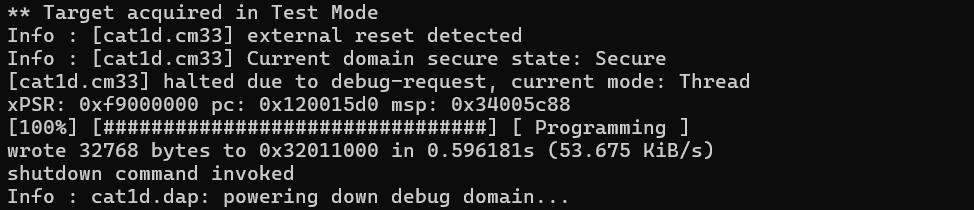
flash read_bank
Reads the
length
bytes from the flash bank
num
starting at
offset
and writes the contents to the binary
filename
. The
num
parameter is a value shown by flash banks.
flash read_bank <num> <filename> <offset> <length>
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Reads the 32-KB block of bank #0 memory and writes it to the binary file:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash read_bank 0 read_bank_0.bin 0x0 0x2000; shutdown"
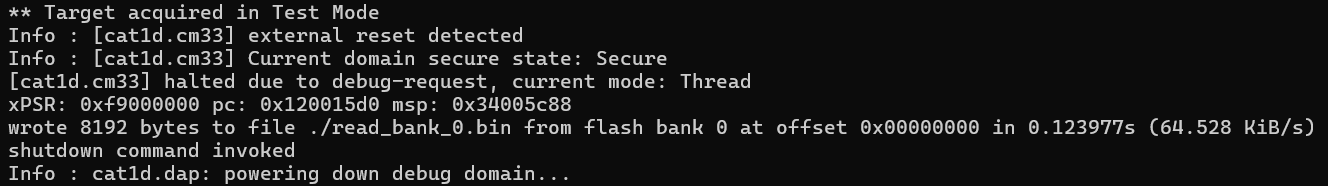
flash verify_bank
Compares the contents of the binary file
filename
with the contents of the flash
num
starting at
offset
. Fails if the contents do not match. The
num
parameter is a value shown by flash banks.
flash verify_bank <num> <filename> <offset>
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Verifies the content of bank #0.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash verify_bank 0 c:/firmware/firmware.bin 0x0; shutdown"
flash padded_value
Sets the default value used for padding any image sections.
flash padded_value <num> <value>
This should normally match the flash bank erased value. If not specified by this command or the flash driver, it defaults to 0xff.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Sets a padded value to 0xFF for bank #0.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash padded_value 0 0xFF; shutdown"
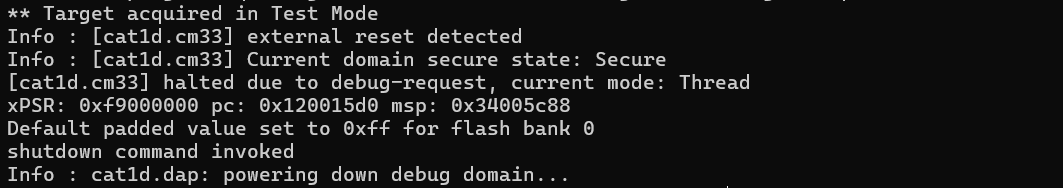
flash rmw
The command is intended to modify flash individual bytes.
flash rmw <address> <data>
The command can be used to program the data to an arbitrary flash address preserving all data that belongs to the same flash sector.
address
– The start address for the programming.
data
Note:
The
flash rmw
command is a custom command implemented in ModusToolbox™ OpenOCD CLI to extend its functionality.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Modifies 8 bytes of the PSOC™ 6 MCU flash at address 0x10001234.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; flash rmw 0x32011234 DEADBEEFBAADC0DE; shutdown"
add_verify_range
The command allows specifying memory regions to be compared during the
verify
operation.
add_verify_range <target> <address> <size>
By default, when no regions are defined, all the regions present in the firmware image file are compared with the corresponding target memory. This breaks the verification process for some non-memory-mapped regions such as EFuses. When the target has at least one
verify
region specified, only data that belongs to that
verify
region is verified.
target
– The target device to assign verify regions.
address
– The start address of the region.
size
– The size of the region, in bytes.
Note:
The
add_verify_range
command is a custom command implemented in ModusToolbox™ OpenOCD CLI to extend its functionality.
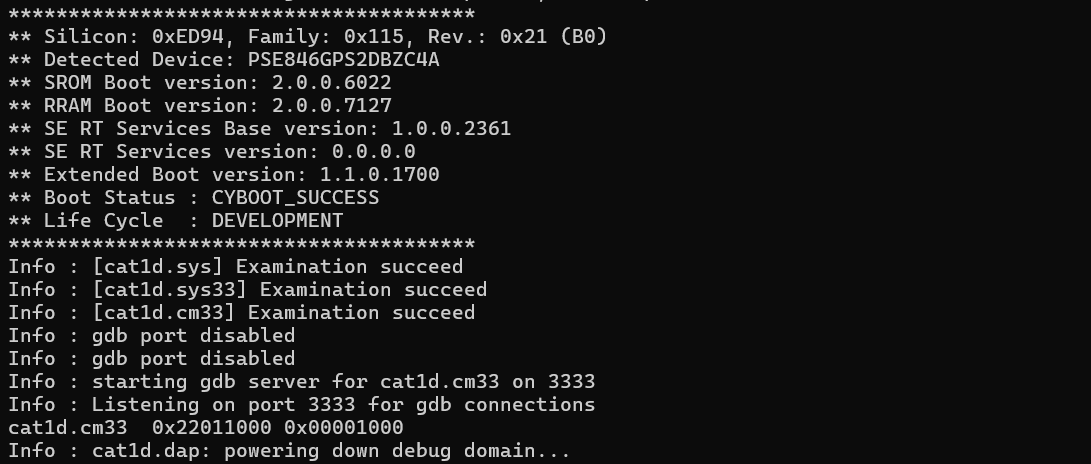
show_verify_ranges
This command displays all active verify ranges for all targets that were added using the
add_verify_range
command. This command does not take any arguments.
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
openocd -s scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; show_verify_ranges; add_verify_range cat1d.cm33 0x22011000 0x1000; show_verify_ranges; exit"
Note:
The
show_verify_ranges
command is a custom command implemented in ModusToolbox™ OpenOCD CLI to extend its functionality.
clear_verify_ranges
This command deletes all verify ranges for the specified target that were added using the
add_verify_range
command.
clear_verify_ranges <target>
Note:
The clear_verify_ranges command is a custom command implemented in ModusToolbox™ OpenOCD CLI to extend its functionality.
verify_image
Verifies
filename
against the target memory starting at
address
. The file format may optionally be specified (bin, ihex, or elf). This will first attempt a comparison using a CRC checksum; if that fails, it will try a binary compare.
verify_image <filename> <address> [bin|ihex|elf]
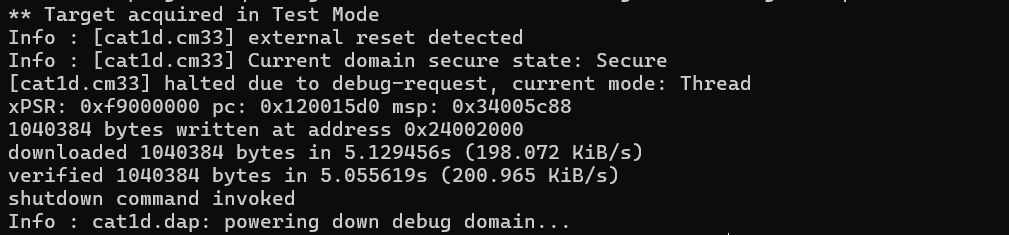
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Verifies a
firmware.hex
image against the target memory.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; load_image c:/firmware/firmware.hex; verify_image c:/firmware/firmware.hex; shutdown"
verify_image_checksum
Verifies
filename
against the target memory starting at
address
. The file format may optionally be specified (bin, ihex, or elf). This perform a comparison using a CRC checksum only.
verify_image_checksum <filename> <address> [bin|ihex|elf]
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU):
Verifies a
firmware.hex
image against the target memory of the PSOC™ Edge MCU using the CRC checksum only.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/jlink.cfg -c "transport select swd" -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; verify_image_checksum d:/firmware.hex 0x0; shutdown"
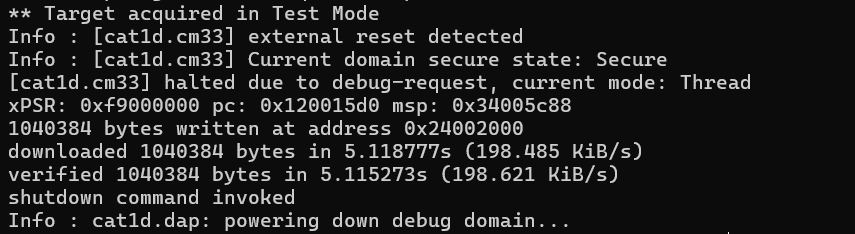
load_image
Loads an image from file
filename
to the target memory offset by
address
from its load address. The file format may optionally be specified (bin, ihex, elf, or s19). Also, the following arguments may be specified:
min_addr– Ignore the data below min_addr (this is w.r.t. to the target's load address + address)max_length
– Maximum number of bytes to load
load_image filename address [[bin|ihex|elf|s19] min_addr max_length]
Example:
Loads the binary file firmware.bin to the RAM of the PSOC™ Edge MCU.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "init; reset init; load_image c:/firmware/firmware.bin 0x22110000; shutdown"
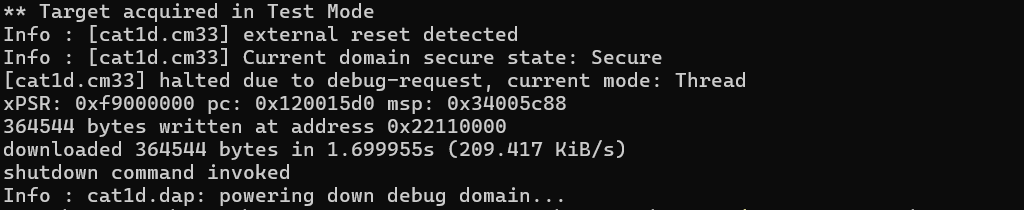
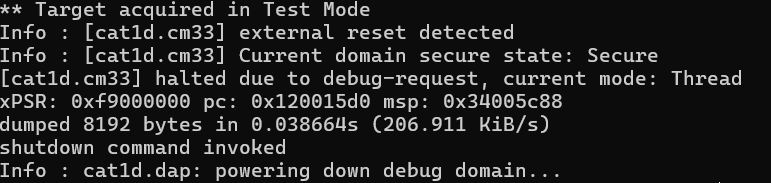
dump_image
Dumps
size
bytes of the target memory starting at address to the binary file named
filename
.
dump_image <filename> <address> size
Example:
Dumps 8 KB of the PSOC™ Edge MCU memory to the file
dump_mem.bin
.
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/cy8c6xxx.cfg -c "init; reset init; dump_image d:/dump_mem.bin 0x10001234 0x2000; shutdown"