Command-line options
OpenOCD command-line options can be combined in a single command-line.
The most important options and commands include:
Option | Description |
|---|---|
Specifies the configuration file to use | |
Specifies the directory to search for configuration files | |
Executes an OpenOCD command. See OpenOCD Commands Overview for details. | |
Specifies the debug level | |
Redirects the log output to the file | |
Displays the help message | |
Displays the OpenOCD version |
--file (-f)
Specifies the configuration file to use.
Multiple configuration files can be specified from a command line. They are interpreted in the order they are specified in the command line.
openocd -f <filename.cfg>
openocd -f interface/ADAPTER.cfg -f target/TARGET.cfg
Example:
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/jlink.cfg -c "transport select jtag" -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg
The output should appear similar to the following:
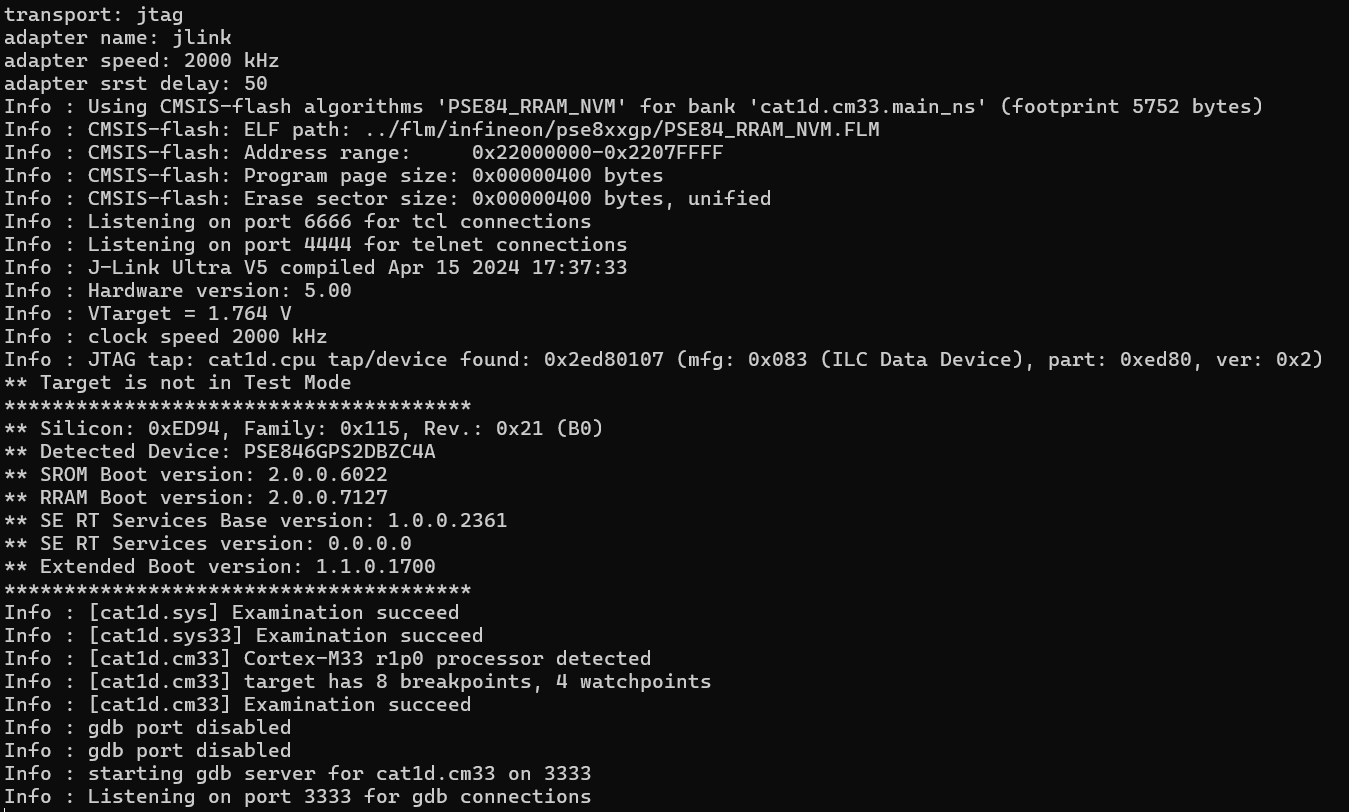
The "tap/service found" message should appear with no warnings, which means the JTAG communication is working.
--search (-s)
Specifies the directory to search for configuration files.
Multiple -s options can be specified. Configuration files and scripts are searched for in the following paths:
the current directory
any search directory specified on the command line using the -s option
any search directory specified using the add_script_search_dir command
$HOME/.openocd (not on Windows)
a directory in the OPENOCD_SCRIPTS environment variable (if set)
the site-wide script library $pkgdatadir/site
the OpenOCD-supplied script library $pkgdatadir/scripts.
The file first found with a matching file name is used.
openocd -s <directory>
Example (J-Link & PSOC™ Edge MCU target):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/jlink.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg
In this example, the -s option specifies the relative path to the directory where the interface and target configurations are located.
--command (-c)
Executes the Tcl command(s).
Multiple commands can be executed by either specifying the multiple -c options or passing several commands to the single -c options. In the latter case, separate the commands with a semicolon.
openocd -c <command>
openocd -c <"command1; command2; …">
Example (J-Link & PSOC™ Edge MCU target):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/jlink.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -c "targets; shutdown"
--debug (-d)
Specifies the debug level. The debug level is 2 by default.
openocd -d<n>
This affects the kind of messages sent to the server log:
Level 0: Error messages only
Level 1: Level 0 messages + warnings
Level 2: Level 1 messages + informational messages
Level 3: Level 2 messages + debugging messages
Example:
openocd -d1
--log_output (-l)
Redirects the log output to the file
logfile.txt
.
openocd -l <logfile.txt>
Example (KitProg3 & PSOC™ Edge MCU target):
openocd -s ../scripts -f interface/kitprog3.cfg -f target/infineon/pse84xgxs2.cfg -l log.txt -c "targets; shutdown"
--help (-h)
Displays the help message.
openocd -h
--version (-v)
Displays the OpenOCD version.
openocd -v