Launch the QSPI Configurator
There are numerous ways to launch the QSPI Configurator, and those ways depend on how you use the various tools in ModusToolbox™ software.
make command
As described in the
tools package user guide
build system chapter, you can run numerous make commands in the application directory, such as launching the QSPI Configurator. After you have created a ModusToolbox™ application, navigate to the application directory and type the following command in the appropriate bash terminal window:
make qspi-configurator
This command opens the QSPI Configurator GUI for the specific application in which you are working.
VS Code and Eclipse
VS Code and Eclipse have tools to launch the QSPI Configurator from within an open application. Refer to the applicable user guide for more details:
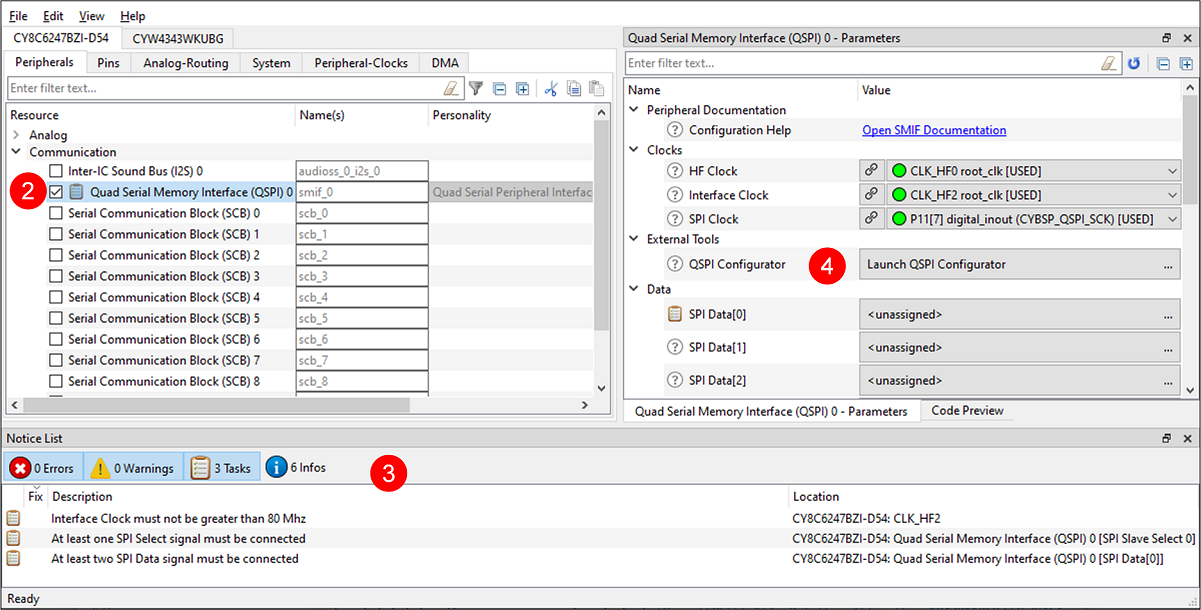
From the Device Configurator
You can also launch the QSPI Configurator from the Device Configurator:
Open the Device Configurator. See the
Device Configurator user guide
for details.
On the
Peripherals
tab, enable the
QSPI
resource.
Optionally, review and resolve the tasks in the Notice List pane. These can be resolved later.
On the
Parameters
tab, click the
Launch QSPI Configurator
button.
Executable (GUI)
If you don't have an application or if you just want to see what the configurator looks like, you can launch the QSPI Configurator GUI by running its executable as appropriate for your operating system (for example, double-click it or select it using the Windows
Start
menu). By default, it is installed here:
<Install_dir>/ModusToolbox/tools_<version>/qspi-configurator-<version>
When launched this way, the QSPI Configurator opens without any memories configured.
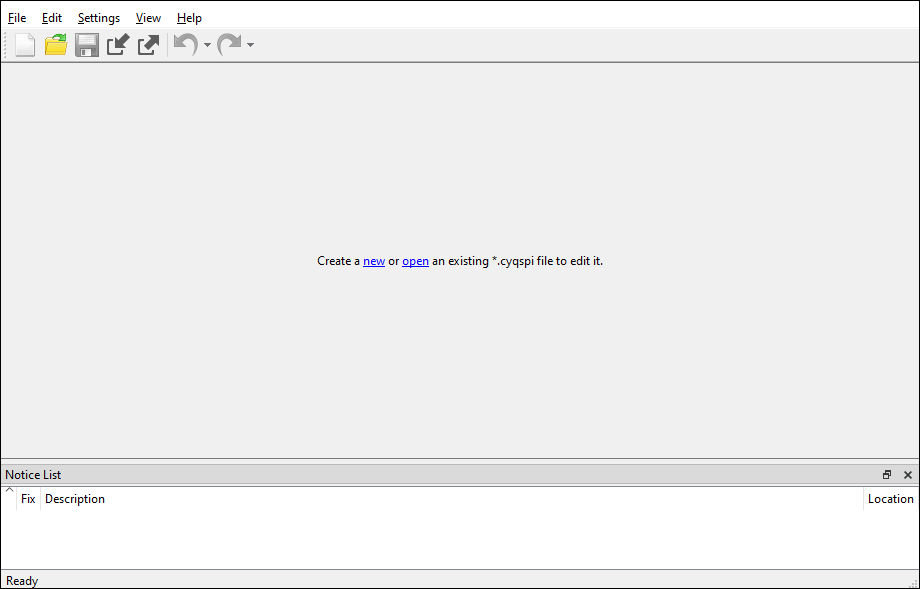
You can either open a specific Configuration file or create a new one. See
Menus
for more information.
Executable (CLI)
The QSPI Configurator executable can be run from the command line, and it also has a "cli" version of the executable as well. Running configurator executables from the command line can be useful as part of batch files or shell scripts to re-generate the source code based on the latest configuration settings. The exit code for the executable is zero if the operation is successful, or non-zero if the operation encounters an error. For more information about the command-line options, run the executable using the
-h
option.