What's in a BSP
This section presents an overview of the key resources that are part of a BSP. Applications can share libraries. BSPs are owned by an application. For more details about library management, refer to the
Library Manager user guide.
The following shows a typical PSOC™ Control BSP located in the
bsps
subdirectory.
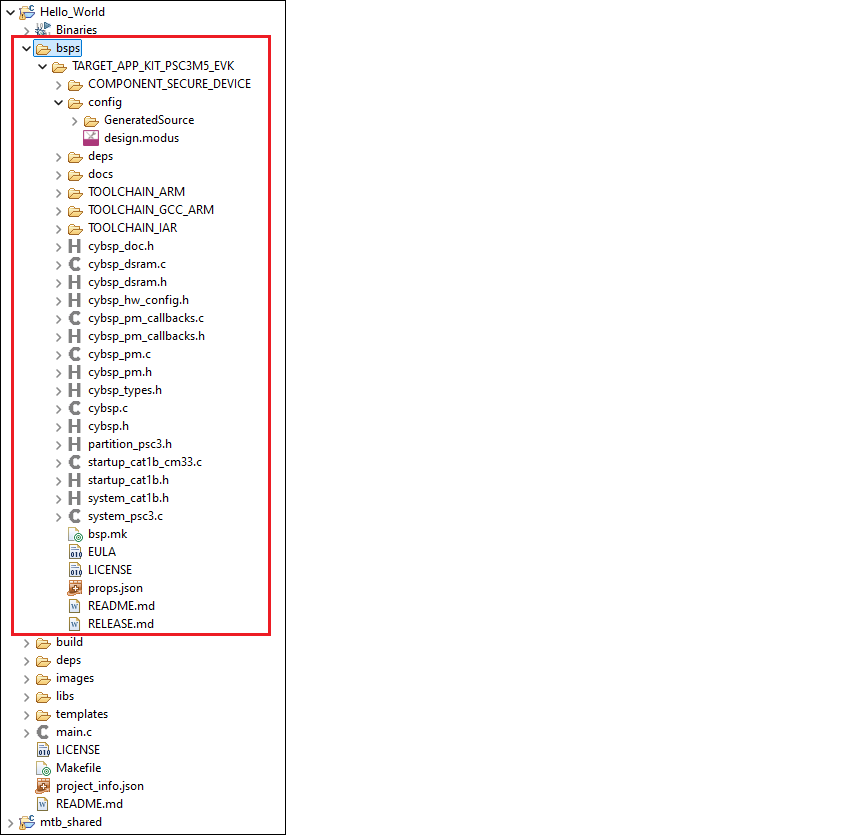
The following sections describe the various files and directories in a typical BSP:
TARGET
This is the top-level directory for a BSP. All BSPs begin with "TARGET" and this is referenced in the application
Makefile
for the active BSP.
config
This directory contains the configuration files (such as
design.modus
) for use with various BSP configurator tools, including Device Configurator, QSPI Configurator, and CAPSENSE™ Configurator. At the start of a build, the build system invokes these tools to generate the source files in the
GeneratedSource
directory.
COMPONENT
Some applications may have "COMPONENT" subdirectories. These directories are conditional, based on what the BSP is being built for. For example, the PSOC™ 6 BSPs include
COMPONENT
directories to restrict which files are used when building for the Arm® Cortex M4 or M0+ core.
deps subdirectory
The
deps
subdirectory inside the BSP contains .
mtbx
files for various library dependencies for the BSP.
docs subdirectory
The
docs
subdirectory contains the documentation in HTML format for the selected BSP.
Support files
Different BSPs will contain various files, such as the API interface to the board's resources. For example, a typical PSOC™ 6 BSP contains the following:
c
ybsp.c /.h
– You need to include only
cybsp.h
in your application to use all the features of a BSP. Call
cybsp_init ()
from
cybsp.c
to initialize the board.
cybsp_types.h
– This currently contains Doxygen comments. It is intended to contain the aliases (macro definitions) for all the board resources, as needed.
system_psoc6.h
– This file provides information about the chip initialization that is done pre-
main()
.
bsp.mk
This file defines the
DEVICE
and other BSP-specific make variables such as
COMPONENTS
. These are described in the
ModusToolbox™ build system
chapter. This file also defines board-specific information such as the device ID, compiler and linker flags, pre-builds/post-builds, and components used with this board implementation.
README/RELEASE.md
These are documentation files. The
README.md
file describes the BSP overall, while the
RELEASE.md
file covers changes made to version of the BSP.
BTSDK-specific BSP files
BTSDK BSPs may optionally provide the following types of files:
wiced_platform.h
– Platform specific structures to define hardware information such as max number of GPIOs, LEDs or.user buttons available
Makefile
– Provided to support LIB flow applications (BTSDK 2.7 and earlier). Not used in MTB flow BTSDK 2.8 or later applications.
*.
hex
– binary application image files that are used as part of the embedded application creation, program, and/or OTA (Over-The-Air) upgrade processes.
platform*.c/h
– Platform specific source and header files used by platform and application initialization functions.
<BSP_NAME>*.cgs
– Patch configuration records in text format, can be multiple copies supporting various board configurations.
<BSP_NAME>*.btp
– Configuration options related to building and programming the application image, can be multiple copies supporting various board configurations.